Project overview
Development of Carbon Farming in the Central Europe
Carbon farming is the process of changing agricultural practices to increase the amount of carbon stored in the soil, or to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from livestock. It has huge potential but is still underused in central Europe. The Carbon Farming – CE project wants to change this and make regions more familiar with the concept. The partnership adapts and tests various techniques and business models and develops a monitoring tool for transnational, standardised carbon sequestration.
-
2,25m €
-
Project Budget
-
80%
-
of the Budget is funded by ERDF
-
9
-
Countries
-
9
-
Regions
-
11
-
Partners
-
7
-
Pilots
Duration
Start date
End date
Project progress
Project partnership
Project partners

Lead partner
Agricultural Institute of Slovenia
Project partner
Knowledge Transfer Division (vocational training, adult education and farm advisory unit of GAK)
DEPARTMENT OF BIOECONOMY AND SYSTEMS ANALYSIS
Department of Forage Crops Breeding and Genetics
Agricultural Chemistry and Pedology Units
Department of Agronomy
Roadmap
Challenge

Embarking on the journey towards climate neutrality, our challenge lies in the innovative transformation of agriculture. Our mission is to contribute significantly by developing unique solutions for capturing CO2 from the air and seamlessly deploying it into the soil. The focal point of this challenge involves introducing and fostering the widespread adoption of "carbon farming" practices, crafting a dynamic business model, implementing effective monitoring solutions, and formulating policies dedicated to storing Greenhouse Gases (GHG) as soil organic carbon (SOC).
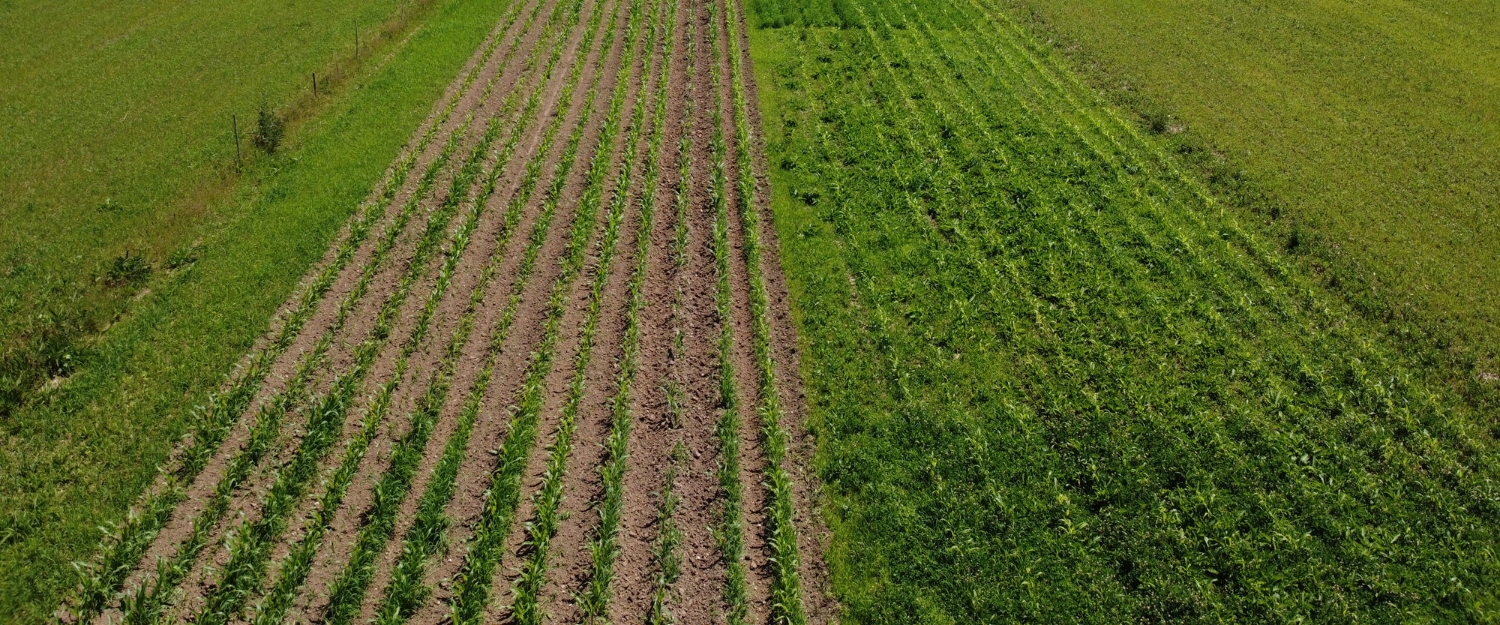
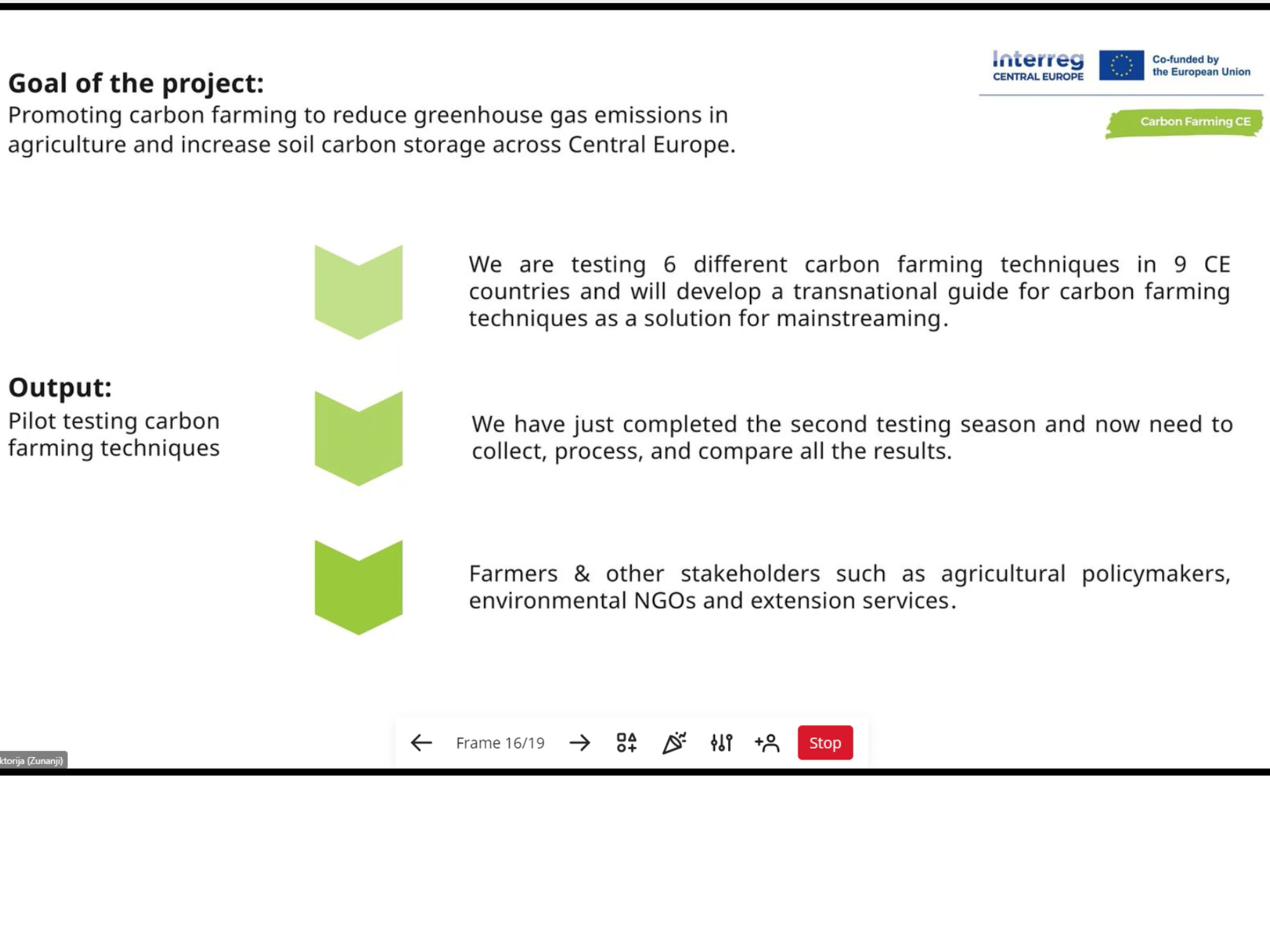
Testing carbon farming techniques

We will test 6 different carbon farming techniques in 9 CE countries and develop a transnational guide for carbon farming techniques as a solution for mainstreaming for 45 farmers.
Testing of carbon farming business models

Evaluation of 5 types of carbon farming business models in the 9 Central European countries. Using the test results to develop transnational practices for carbon farming business models and upscaling of successful models.
Carbon farming mainstreaming

Develop a standardized monitoring methodology for carbon sequestration and measures to promote carbon farming policies to achieve broad acceptance and implementation.
News
Events
Pilot actions
Outputs

Pilot testing carbon farming techniques
CE guide for carbon farming techniques to minimize CO2 and improve soil quality

Pilot testing carbon farming business models
Carbon farming business model procedures

Strategy and action plan for mainstreaming of carbon farming

Partners and associated partners cooperating together
Project videos
Project documents
Deliverable
Press Release
Carbon Farming Monitoring Strategy roadmap
Communication Package
Project images
Carbon Farming CE
The project lead partner is responsible for the content of this project website.